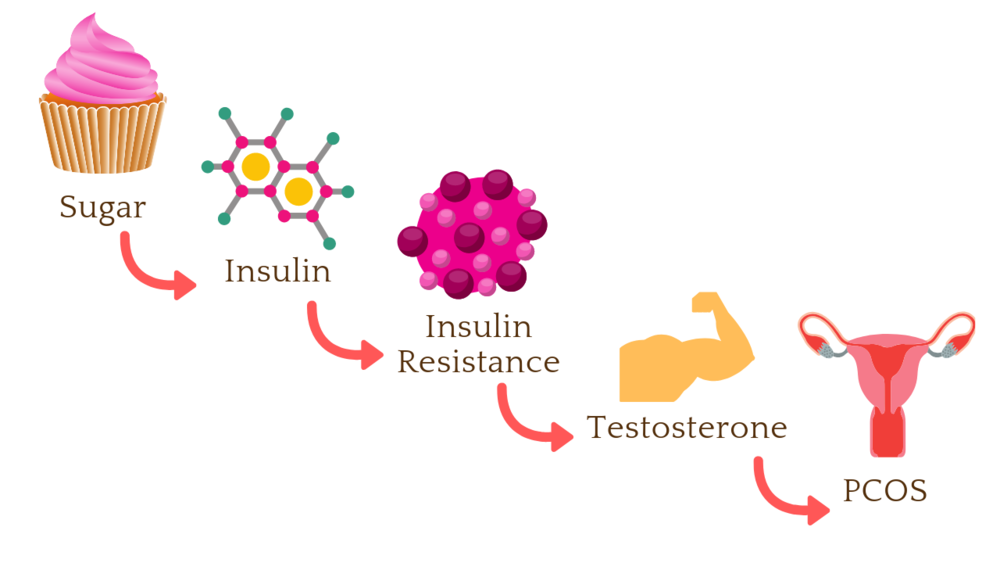
Metformin For PCOS
Metformin is a medication commonly prescribed to treat Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It works by reducing insulin resistance, which is often present in women with PCOS. Metformin helps to regulate menstrual cycles, lower androgen levels, and improve fertility in women with PCOS. It can also be effective in managing symptoms such as acne and excess hair growth. Metformin For PCOS is typically taken orally, and the dosage and duration of treatment may vary depending on the individual’s response to the medication. While metformin can be a helpful treatment option for PCOS, it may cause side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, and stomach upset. Therefore, it’s important to discuss any potential risks and benefits of metformin with a healthcare provider before starting treatment.
Benefits Of Metformin For PCOS
Here are some benefits of metformin for PCOS:
Improved insulin sensitivity: Women with PCOS often have insulin resistance, which can lead to elevated blood glucose levels and increased risk of type 2 diabetes. Metformin helps to improve insulin sensitivity, leading to better glucose control. A study of 43 women with PCOS found that metformin reduced fasting insulin levels by 22% after six months of treatment.
Regular menstrual cycles: Women with PCOS often experience irregular menstrual cycles due to hormonal imbalances. Metformin can help to regulate menstrual cycles by reducing androgen levels and improving ovulation. A meta-analysis of 16 randomized controlled trials found that metformin increased the rate of ovulation by 2.5 times compared to placebo.
Improved fertility: Metformin can also improve fertility in women with PCOS. A systematic review of 11 randomized controlled trials found that metformin increased the likelihood of pregnancy by 53% compared to placebo.
Reduced risk of gestational diabetes: Women with PCOS have an increased risk of gestational diabetes during pregnancy. Metformin has been shown to reduce the risk of gestational diabetes in women with PCOS. A meta-analysis of 14 randomized controlled trials found that metformin reduced the risk of gestational diabetes by 36% compared to placebo or no treatment.
Management of symptoms: Metformin can also help to manage symptoms of PCOS such as acne, excess hair growth, and weight gain. A randomized controlled trial of 61 women with PCOS found that metformin improved acne and hirsutism (excess hair growth) compared to placebo.
Reduced risk of cardiovascular disease: Women with PCOS have a higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease, and metformin may help to reduce this risk. A meta-analysis of 14 randomized controlled trials found that metformin improved markers of cardiovascular risk such as triglycerides and total cholesterol.
Improved mental health: Women with PCOS may be at higher risk of depression and anxiety. A randomized controlled trial of 54 women with PCOS found that metformin improved symptoms of depression compared to placebo.
Reduced risk of cancer: Women with PCOS have a higher risk of certain types of cancer, such as endometrial and ovarian cancer. Metformin may help to reduce this risk. A meta-analysis of 22 observational studies found that metformin was associated with a reduced risk of endometrial cancer.
Improved quality of life: PCOS can have a significant impact on a woman’s quality of life. Metformin can help to improve quality of life by reducing symptoms such as acne, hirsutism, and menstrual irregularity. A randomized controlled trial of 40 women with PCOS found that metformin improved quality of life compared to placebo.
Cost-effective treatment: Metformin is a relatively inexpensive medication, making it a cost-effective treatment option for women with PCOS. A study of 165 women with PCOS found that metformin was more cost-effective than clomiphene citrate (a commonly used fertility medication) for improving fertility outcomes.
Overall, metformin is a versatile medication that can offer a range of benefits for women with PCOS, including improved insulin sensitivity, menstrual regulation, fertility, and management of symptoms. It may also have additional benefits such as reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease, cancer, and improving mental health and quality of life.
What To Expect When Taking Metformin For PCOS
Here’s what you can expect when taking metformin for PCOS:
Improved insulin sensitivity: Metformin helps to improve insulin sensitivity by reducing the amount of glucose produced by the liver and increasing the uptake of glucose by cells in the body. A meta-analysis of 14 randomized controlled trials found that metformin improved insulin sensitivity in women with PCOS.
Menstrual regulation: Many women with PCOS have irregular menstrual cycles, which can impact fertility. Metformin can help to regulate menstrual cycles by reducing insulin resistance and improving hormone levels. A meta-analysis of 18 randomized controlled trials found that metformin improved menstrual regularity in women with PCOS.
Improved fertility: Metformin can improve fertility in women with PCOS by regulating menstrual cycles and improving insulin sensitivity. A meta-analysis of 24 randomized controlled trials found that metformin improved ovulation and pregnancy rates in women with PCOS.
Possible side effects: Like all medications, metformin can have side effects. The most common side effects of metformin include gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. These symptoms usually improve over time and can be minimized by starting with a low dose and gradually increasing it. Rarely, metformin can cause a serious side effect called lactic acidosis, which can be life-threatening.
Dosage and administration: Metformin is usually taken orally in tablet form. The starting dose is typically 500 mg once or twice daily, and the dose can be increased gradually over several weeks to a maximum of 2,000 mg per day. It is important to take metformin with food to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal side effects.
Overall, taking metformin for PCOS can help to improve insulin sensitivity, regulate menstrual cycles, and improve fertility. However, it is important to be aware of possible side effects and to take the medication as directed by your healthcare provider.
How To Take Metformin For PCOS
Here’s how to take metformin for PCOS:
Starting Start with a low dose: Metformin is usually started at a low dose, such as 500 mg once or twice daily. with a low dose can help to minimize side effects such as gastrointestinal symptoms.
Take with food: It is important to take metformin with food to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal side effects. Taking metformin with a meal can also help to slow down the absorption of the medication, which can help to reduce the risk of side effects.
Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions: Your healthcare provider will determine the appropriate dose of metformin for you based on your individual needs and medical history. It is important to follow their instructions carefully and not to exceed the recommended dose.
Take consistently: It is important to take metformin consistently, at the same time(s) each day. This can help to ensure that you are getting the full benefit of the medication and can also help to minimize side effects.
Monitor blood sugar levels: If you have diabetes or prediabetes, it is important to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly while taking metformin. Your healthcare provider may recommend adjusting your medication dose or other diabetes management strategies based on your blood sugar levels.
Be aware of possible side effects: Like all medications, metformin can have side effects. The most common side effects of metformin include gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. These symptoms usually improve over time and can be minimized by starting with a low dose and gradually increasing it.
Give it time: It can take several weeks to a few months for metformin to start working effectively. Be patient and continue to take the medication as directed by your healthcare provider.
Do not crush or chew: Metformin tablets should be swallowed whole and should not be crushed or chewed. This can affect the way the medication is absorbed by the body.
Do not skip doses: It is important to take metformin as directed by your healthcare provider and not to skip doses. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless it is close to the time for your next dose. In that case, skip the missed dose and continue with your regular dosing schedule.
Inform your healthcare provider of other medications: It is important to inform your healthcare provider of any other medications, supplements, or vitamins that you are taking. Some medications can interact with metformin and affect how it works in the body.
Be aware of alcohol consumption: It is important to be aware of alcohol consumption while taking metformin. Drinking alcohol can increase the risk of lactic acidosis, which is a rare but serious side effect of metformin.
Stay hydrated: It is important to stay hydrated while taking metformin. Drink plenty of water and other fluids to help prevent dehydration and to minimize the risk of gastrointestinal side effects.
Remember to always consult with your healthcare provider if you have any questions or concerns about taking metformin for PCOS. They can provide you with personalized guidance and advice to help you manage your condition effectively.
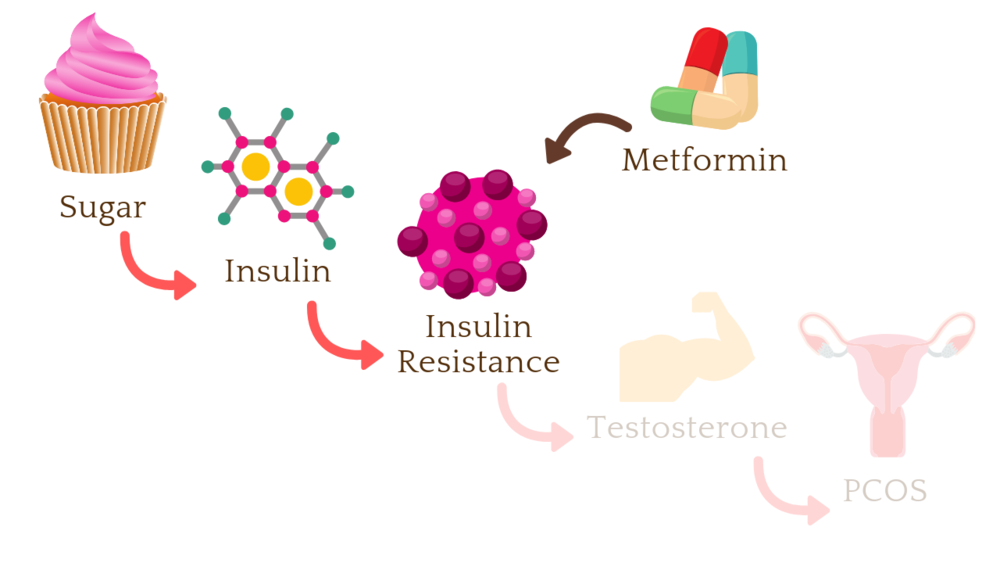
Metformin For PCOS Reviews
Here are some reviews of metformin for PCOS:
1. A meta-analysis of 14 randomized controlled trials found that metformin significantly improved insulin resistance in women with PCOS.
2. A meta-analysis of 18 randomized controlled trials found that metformin improved menstrual regularity in women with PCOS.
3. A meta-analysis of 24 randomized controlled trials found that metformin improved ovulation and pregnancy rates in women with PCOS.
4. A systematic review of 36 studies found that metformin improved insulin resistance, menstrual regularity, and fertility outcomes in women with PCOS.
5. A randomized controlled trial found that metformin reduced the risk of developing gestational diabetes in pregnant women with PCOS.
6. A review of 20 randomized controlled trials found that metformin improved insulin sensitivity, decreased androgen levels, and improved menstrual regularity in women with PCOS.
7. A meta-analysis of 10 randomized controlled trials found that metformin improved fasting insulin levels, HOMA-IR (a measure of insulin resistance), and androgen levels in women with PCOS.
8. A systematic review and meta-analysis of 20 randomized controlled trials found that metformin improved ovulation and pregnancy rates in women with PCOS undergoing assisted reproductive technologies (ART), such as in vitro fertilization (IVF).
9. A randomized controlled trial found that combining metformin with clomiphene citrate (a medication used to induce ovulation) improved pregnancy rates compared to clomiphene citrate alone in women with PCOS.
10. A meta-analysis of 14 randomized controlled trials found that metformin reduced body weight and body mass index (BMI) in women with PCOS.
Overall, the evidence suggests that metformin can be an effective treatment for PCOS, improving insulin sensitivity, menstrual regularity, and fertility outcomes. However, it is important to note that individual responses to metformin can vary, and some women may not experience significant improvements in their symptoms. Additionally, as with any medication, metformin can have side effects and should be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Foods To Avoid When Taking Metformin For PCOS
When taking metformin for PCOS, there are certain foods that may affect how well the medication works or increase the risk of side effects. Here are some foods to avoid or limit while taking metformin:
High-carbohydrate foods: Eating foods that are high in carbohydrates, especially simple sugars, can increase blood glucose levels and reduce the effectiveness of metformin. It is important to limit or avoid foods like candy, soda, juice, white bread, and pasta.
Alcohol: Drinking alcohol can increase the risk of lactic acidosis, a rare but serious side effect of metformin. It is recommended to avoid alcohol or limit it to no more than one drink per day.
Fatty or fried foods: High-fat foods can slow down the absorption of metformin and reduce its effectiveness. Additionally, consuming too much fat can increase the risk of gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
Grapefruit: Grapefruit and grapefruit juice can increase the levels of metformin in the body, which can increase the risk of side effects. It is best to avoid grapefruit while taking metformin.
Caffeine: Caffeine can increase the risk of lactic acidosis in people taking metformin. It is recommended to limit caffeine intake to no more than 400 milligrams per day, which is equivalent to about four cups of coffee.
Vitamin B12: Long-term use of metformin can decrease the absorption of vitamin B12, which can lead to a deficiency. It is recommended to have your vitamin B12 levels checked regularly and to supplement if necessary.
Calcium: Calcium supplements can interfere with the absorption of metformin and reduce its effectiveness. It is recommended to take calcium supplements at least two hours before or after taking metformin.
High-protein foods: Consuming a high-protein meal or snack can reduce the absorption of metformin and reduce its effectiveness. It is recommended to avoid consuming high-protein foods at the same time as taking metformin.
Acidic foods and beverages: Consuming acidic foods and beverages, such as citrus fruits, tomatoes, and vinegar, can increase the acidity of the stomach and reduce the absorption of metformin. It is recommended to consume these foods and beverages in moderation and at least two hours before or after taking metformin.
Chromium: Chromium supplements may increase the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) in people taking metformin. It is recommended to avoid chromium supplements while taking metformin.
Overall, it is important to follow a healthy and balanced diet while taking metformin for PCOS. This may include foods that are low in carbohydrates, high in fiber, and rich in nutrients like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
What Happens If You Miss A Dose Of Metformin For PCOS
- If you miss a dose of metformin for PCOS, it is important to take it as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for your next dose, it is recommended to skip the missed dose and continue with your regular dosing schedule. Taking a double dose to make up for a missed dose can increase the risk of side effects.
- Missing a dose of metformin can affect how well the medication works in controlling blood glucose levels and managing PCOS symptoms. It is important to take metformin as prescribed by your healthcare provider to achieve the maximum benefits.
In addition, missing doses of metformin can increase the risk of developing complications associated with PCOS, such as insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. It is important to maintain a consistent dosing schedule and to communicate with your healthcare provider if you are experiencing difficulty taking your medication as prescribed.
Ozempic vs Metformin For PCOS
| Ozempic | Metformin | |
| Type of Medication | GLP-1 Receptor Agonist | Biguanide |
| Mechanism of Action | Increases insulin secretion, decreases glucagon secretion, slows gastric emptying | Decreases hepatic glucose production, increases insulin sensitivity, decreases glucose absorption in the intestine |
| Administration | Subcutaneous injection once a week | Oral tablet once or twice daily |
| Starting Dosage | 0.25 mg once a week | 500 mg once or twice daily |
| Maximum Dosage | 1 mg once a week | 2000 mg per day |
| Weight Loss | Can lead to significant weight loss | Can lead to modest weight loss |
| Hypoglycemia Risk | Low, but can increase when used with other diabetes medications | Low, but can increase when used with other diabetes medications |
| Gastrointestinal Side Effects | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort |
| Vitamin B12 Deficiency | Can increase the risk of vitamin B12 deficiency | Can decrease the absorption of vitamin B12 |
| Cost | Expensive | Affordable |
It is important to note that the choice of medication for PCOS should be individualized and based on various factors, such as the severity of symptoms, presence of comorbidities, medication cost, and patient preference. It is recommended to discuss the options with your healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan for you.
How Long To Take Metformin For PCOS
- The length of time to take metformin for PCOS can vary depending on individual factors such as the severity of symptoms, response to treatment, and presence of comorbidities. Metformin is typically prescribed as a long-term treatment for PCOS to help manage symptoms and prevent complications such as insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
- Studies have shown that metformin can be effective in improving menstrual regularity, reducing androgen levels, and promoting weight loss in women with PCOS. However, the optimal duration of treatment with metformin is not yet established.
- In general, it is recommended to continue taking metformin for PCOS as long as it is providing benefits and is well-tolerated. Your healthcare provider may periodically evaluate your response to treatment and adjust the dosage or duration of therapy as needed.
It is important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions and continue taking metformin as prescribed, even if you start feeling better or your symptoms improve. Stopping or changing the medication without medical advice can lead to a recurrence of symptoms and complications.
Metformin For PCOS Without Diabetes
Metformin is commonly used as an off-label treatment for PCOS in women who do not have diabetes. PCOS is a hormonal disorder that affects up to 10% of women of reproductive age, and it is characterized by a variety of symptoms such as irregular periods, infertility, excessive hair growth, and acne. Metformin is a medication that works by reducing insulin resistance, which is a common feature of PCOS. Insulin resistance can cause the ovaries to produce too much androgen hormone, which can lead to the development of PCOS symptoms. By reducing insulin resistance, metformin can help to regulate menstrual cycles, reduce androgen levels, and improve fertility in women with PCOS.
Several clinical trials have investigated the use of metformin in women with PCOS who do not have diabetes. These studies have shown that metformin can be effective in improving menstrual regularity, reducing androgen levels, and promoting weight loss in this population. However, the optimal dosage and duration of treatment with metformin in non-diabetic women with PCOS is not yet established. It is important to note that metformin is not a cure for PCOS, and it should be used in combination with lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, healthy diet, and weight management to achieve optimal results. Metformin can cause side effects such as gastrointestinal disturbances, vitamin B12 deficiency, and lactic acidosis, especially at high doses or in individuals with kidney or liver disease.
Therefore, the decision to use metformin for PCOS without diabetes should be individualized and based on a thorough evaluation of the benefits and risks of treatment. It is recommended to discuss the options with your healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan for you. Metformin is a commonly used medication for the treatment of PCOS in women without diabetes. Here are some additional facts and figures about metformin for PCOS without diabetes:
Metformin can help to regulate menstrual cycles: Women with PCOS often experience irregular menstrual cycles due to hormonal imbalances. Metformin can help to regulate menstrual cycles by reducing insulin resistance and improving ovulation.
Metformin can improve fertility: Women with PCOS often have difficulty getting pregnant due to irregular menstrual cycles and hormonal imbalances. Metformin can improve fertility by regulating menstrual cycles and promoting ovulation.
Metformin can reduce androgen levels: Women with PCOS often have high levels of androgen hormones, which can cause symptoms such as excessive hair growth and acne. Metformin can reduce androgen levels by reducing insulin resistance and improving hormonal balance.
Metformin can promote weight loss: Women with PCOS often struggle with weight management due to insulin resistance and hormonal imbalances. Metformin can promote weight loss by reducing insulin resistance and improving metabolic function.
Metformin can cause side effects: Like all medications, metformin can cause side effects such as gastrointestinal disturbances, vitamin B12 deficiency, and lactic acidosis. It is important to discuss the risks and benefits of metformin with your healthcare provider before starting treatment.
Metformin should be used in combination with lifestyle modifications: While metformin can be effective in improving PCOS symptoms, it should be used in combination with lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, healthy diet, and weight management to achieve optimal results.
The optimal dosage and duration of treatment with metformin is not established: The optimal dosage and duration of treatment with metformin for PCOS without diabetes is not yet established. It is recommended to discuss the options with your healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan for you.
Overall, metformin can be an effective treatment option for women with PCOS without diabetes. It can help to regulate menstrual cycles, improve fertility, reduce androgen levels, promote weight loss, and improve metabolic function. However, it is important to discuss the risks and benefits of metformin with your healthcare provider before starting treatment.