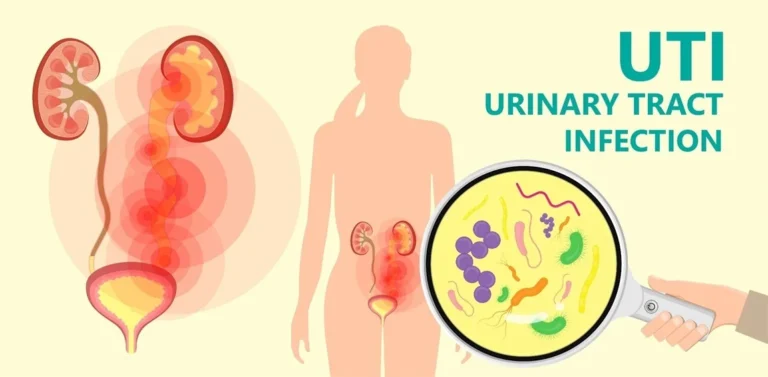
Do you know what the second most common infection affecting women worldwide is? The answer may surprise you – it’s urinary tract infections (UTIs). This painful and often inconvenient condition affects millions of people every year, causing discomfort and inconvenience. But despite its prevalence, UTIs are still not widely understood or talked about.
In this article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about UTIs. From what causes them to how they can be treated and prevented, we’ll delve into all aspects of this frustrating condition. We’ll also look at some of the latest innovations in treating UTIs, including new medications and technologies that could revolutionize how we tackle these infections.
So whether you’ve been dealing with recurring UTIs for years or have just experienced your first bout of symptoms, read on to learn more about this common but misunderstood condition. With a better understanding of UTIs comes a greater chance of preventing future infections and getting relief from current ones.
How Long Do Utis Last
UTIs, or urinary tract infections, are a common ailment that affects millions of people every year. These pesky infections can cause discomfort and pain while urinating, which can be quite unpleasant for anyone who experiences them.
If you’ve ever had a UTI before, then you know how uncomfortable they can be. The good news is that they typically don’t last very long. In fact, most UTIs only last about five to seven days before the symptoms start to subside.
Of course, this doesn’t mean that you should ignore your symptoms if you suspect that you have a UTI. If left untreated, these infections can lead to more serious health problems down the road. So it’s important to seek medical attention as soon as possible if you think that you might have a UTI. Speaking of seeking medical attention, one question that often comes up when dealing with UTIs is whether or not they’re contagious.
Are Utis Contagious
Have you ever found yourself wondering if urinary tract infections (UTIs) are contagious? It’s a common question that comes up when someone is diagnosed with this painful condition. The answer, however, might surprise you.
While UTIs themselves are not contagious, the bacteria that cause them can be spread through sexual activity or poor hygiene practices. This means that while you cannot catch a UTI from someone who has one, there are still ways to contract the infection. For example, if you have sex with someone who has an active UTI, it’s possible for their bacteria to enter your own urethra and cause an infection of your own.
It’s important to note that most UTIs are caused by E.coli bacteria which live in the gut and do not typically pose a serious health risk. However, some strains of E.coli have been known to cause more severe infections such as pyelonephritis which can lead to kidney damage if left untreated. So while UTIs may not be contagious per se, it’s still important to practice good hygiene habits and safe sex practices to avoid contracting these pesky infections.
Now that we’ve established whether or not UTIs are contagious, let’s shift our focus to another common concern: Can recurrent UTIs be a sign of cancer? While it’s true that frequent UTIs can sometimes indicate an underlying medical issue such as bladder or kidney cancer, this is quite rare. More often than not, recurring UTIs simply mean that the initial infection wasn’t fully treated and was able to reoccur.
In fact, women are much more likely to get repeat UTIs due to their anatomy – specifically their shorter urethras which make it easier for bacteria to travel into the bladder. Additionally, certain lifestyle factors like holding in urine for extended periods of time or frequently using irritating feminine products can also increase your chances of developing multiple UTIs over time.
So remember: while UTIs may not be contagious, they can still be a nuisance to deal with. And if you do find yourself experiencing recurrent infections, it’s always best to speak with your healthcare provider who can help determine the underlying cause and provide appropriate treatment options.
Can Recurrent Utis Be A Sign Of Cancer
Did you know that recurrent UTIs could be a sign of cancer? It’s scary to think about, but it is essential to understand the warning signs and how we can protect ourselves. While only a small percentage of UTIs indicate underlying issues such as bladder or kidney cancer, understanding these symptoms can help us take precautions and seek treatment early.
According to the American Cancer Society, less than 1% of all UTIs are caused by bladder or kidney cancer. However, if you experience repeated UTIs within a short period, despite taking antibiotics, this may be an indication of something more serious. Other warning signs include blood in your urine, pain while urinating, frequent urges to use the bathroom without passing much urine each time, and pelvic discomfort.
It is crucial to note that several factors contribute to chronic UTIs other than cancer. For example, women have a shorter urethra than men; hence bacteria travel up quickly from their bladder into their urinary tract system. Ageing also weakens our immune systems making it easier for infections to occur frequently. Therefore prevention measures such as wiping from front to back after using the toilet and staying hydrated should be taken seriously.
In conclusion, while not all recurrent UTIs signify cancer, they are worth investigating further with your doctor. Knowing what causes them helps prevent future occurrences. In the next section let’s discuss some common reasons why people get UTI’s – step right in.
What Causes Utis
Picture this: a winding road that leads to your bladder. Along the way, there are checkpoints guarded by tiny soldiers called bacteria. Sometimes, these guards get too powerful and invade the walls of your urinary tract, causing an infection known as a UTI. But what causes these pesky bacterial attacks in the first place?
UTIs can be caused by different types of bacteria, but most commonly arise from Escherichia coli (E.coli). This bacterium naturally lives in our gut and helps with digestion, but when it migrates to other areas like the urethra or bladder, it becomes problematic. Other factors such as sexual activity, certain medications, weak immune system and catheter use can also increase one’s risk for developing a UTI.
While many people experience a UTI at some point in their life, prevention is key. Drinking plenty of water and urinating frequently can help flush out any potential invaders. Urinating after sex can also help clear out any unwanted bacteria that may have entered during intercourse. Proper hygiene practices such as wiping front-to-back and avoiding irritating feminine products can also reduce one’s susceptibility to UTIs.
But what if you’re already experiencing symptoms? Do UTIs go away on their own? Stay tuned for the next section where we’ll dive into treatment options and how long it typically takes for relief.
Do Utis Go Away
Have you ever experienced a urinary tract infection? It’s like having an army of tiny soldiers invading your body, taking over every inch of it. The constant urge to pee, the burning sensation when urinating – all these symptoms can make anyone feel miserable. But do UTIs go away on their own?
Most of the time, UTIs will clear up with proper treatment. Antibiotics are commonly prescribed by doctors to fight off the bacteria causing the infection. However, if left untreated or not treated properly, UTIs can lead to more severe complications such as kidney infections which require hospitalization.
It’s important to note that while antibiotics may provide relief from symptoms within a few days, it is crucial to complete the full course of medication prescribed by your doctor even after feeling better. This ensures that all bacteria in your system have been eliminated and prevents further recurrence of UTIs. In some cases, lifestyle changes such as drinking plenty of water and avoiding certain irritants can also aid in preventing future infections.
So yes, UTIs do go away but only with proper treatment and care. While they may seem like a minor inconvenience at first, ignoring them can lead to serious health issues down the line. Now that we know this information about how long a UTI lasts let us explore why they keep coming back despite our best efforts at prevention.
Why Do I Keep Getting Utis
Imagine a beautiful garden, lush with greenery and vibrant flowers. But every so often, there’s a weed that pops up and ruins the beauty of the landscape. This is how it can feel for someone who keeps getting urinary tract infections (UTIs). UTIs are like those pesky weeds that keep returning to ruin an otherwise healthy body.
So why do some people seem to be more prone to UTIs than others? There could be a variety of reasons. For women, anatomy plays a role – their urethra is shorter, making it easier for bacteria to travel from the anus to the bladder. Sexual activity can also increase the risk of developing a UTI. Other factors include weakened immune systems or certain medical conditions that affect bladder function.
While antibiotics are often prescribed as treatment for UTIs, they don’t necessarily address the underlying cause of recurring infections. It’s important for individuals who experience frequent UTIs to speak with their healthcare provider about possible causes and preventative measures. This may involve lifestyle changes such as staying hydrated, urinating after sex, and practicing good hygiene habits.
It’s frustrating when something seems out of our control, but taking steps towards preventing recurrent UTIs can help bring back balance to your health and wellbeing. And while it’s commonly thought of as a woman’s issue, men can also get UTIs – which we’ll explore in further detail in the next section.
Can Men Get Utis
Can men get UTIs? Absolutely! Although it is more common for women to contract urinary tract infections, men can also experience this painful and uncomfortable condition. The reason why women are at higher risk of developing a UTI is because their urethra is shorter than that of a man’s, which means bacteria has less distance to travel before reaching the bladder.
However, there are certain factors that can increase a man’s chances of getting a UTI. For example, if you have an enlarged prostate or kidney stones, this can cause blockages in your urinary tract that make it easier for bacteria to grow. Additionally, having unprotected anal sex or poor hygiene habits down below can introduce harmful bacteria into your system and lead to infection.
If you suspect that you may have a UTI as a man, it’s important not to ignore the symptoms. These typically include pain while urinating, frequent urges to pee but difficulty doing so, cloudy urine with an unpleasant smell, and discomfort around your lower abdomen or back. Luckily, treatment usually involves taking antibiotics prescribed by your doctor – just be sure to finish the full course even if you start feeling better sooner.
So now we know that men (and not just women) can get UTIs too – but what about pregnant women? Are they particularly susceptible? Stay tuned to find out whether pregnancy increases one’s likelihood of developing this pesky problem…
Are Utis Common In Pregnancy
Did you know that urinary tract infections (UTIs) are one of the most common bacterial infections during pregnancy? In fact, studies show that up to 10% of pregnant women will experience a UTI at some point in their pregnancy. But why is this so common and what can be done about it?
During pregnancy, hormonal changes cause the bladder and urethra to relax, making it easier for bacteria to travel up into the urinary system. Additionally, as the uterus grows, it puts pressure on the bladder which can make it difficult to fully empty urine from the body. This stagnant urine creates an ideal environment for bacteria growth.
But just because UTIs are common in pregnancy doesn’t mean they should be ignored. Left untreated, a UTI can lead to more serious complications such as kidney infections or preterm labor. It’s important for pregnant women who suspect they may have a UTI to seek medical attention promptly.
So what can be done to prevent UTIs during pregnancy? Drinking plenty of water and urinating frequently can help flush out any potential bacteria before infection occurs. Wiping front-to-back after using the toilet and avoiding harsh soaps or douches in the genital area can also reduce risk. And if a woman does develop a UTI during pregnancy, antibiotics prescribed by her healthcare provider can usually clear up the infection quickly.
Remember, while UTIs may be common during pregnancy, they shouldn’t be taken lightly. By taking preventative measures and seeking prompt treatment when necessary, pregnant women can minimize their risk of developing these uncomfortable infections.
Conclusion
In conclusion, urinary tract infections (UTIs) can be a painful and frustrating experience. So how long do UTIs last? It really depends on the individual case and severity of the infection. However, with proper treatment and care, most UTIs can be cleared up within a few days to a week.
One thing that many people wonder is whether or not UTIs are contagious. The good news is that they are not generally considered contagious like other bacterial infections.
Recurrent UTIs may also raise concerns about possible underlying health issues such as cancer. While this can be worrisome, it’s important to remember that there are many different factors that contribute to recurrent UTIs besides cancer. By taking steps to prevent future infections and seeking medical attention when necessary, you can reduce your risk of developing complications from UTIs.
So why do I keep getting UTIs? This is a common question that many people have. There are several reasons why someone might experience recurring UTIs, including genetics, certain medications, hygiene habits, sexual activity, and more. By working with your healthcare provider to identify potential triggers and develop an effective prevention plan, you can minimize your risk of dealing with frequent UTIs in the future.
Overall, while UTIs may not be the most pleasant topic to discuss, they are quite common and treatable. Whether you’re wondering if men can get them too or if they’re common during pregnancy, the answer is yes, If you suspect that you might have a urinary tract infection or if you’ve been experiencing symptoms for longer than a few days without improvement, don’t hesitate to reach out to your doctor for guidance and support.